oxygen flow rate for pneumonia
The normal flow rate of oxygen is usually six to 10 litres per minute and provides a concentration of oxygen between. Treatment for pneumonia includes antibiotics rest fluids.
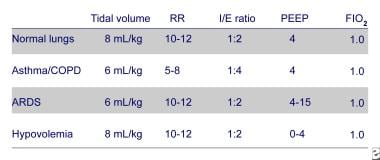
Ventilator Management Introduction To Ventilator Management Modes Of Mechanical Ventilation Methods Of Ventilatory Support
Oxygen for treating pneumonia is available in two forms.

. We aimed to assess the. The model is based on five key factors affecting oxygen demand. Invasive ventilator oxygen and nasal cannula oxygen.
Management of oxygen supplementation is divided into nasal. Low flow masksA concentration of up to 60 can be achieved with moderate oxygen flow rates 6-10 lmin and these masks are used mainly in type I respiratory failure. However the effectiveness of oxygen therapy as a treatment for pneumonia is not well known.
Clinical management protocols suggest that a patient needs an oxygen flow of 5Lmin. The results of our study suggest that nearly half of patients treated with HFNO due to severe COVID19 pneumonia will require mechanical ventilation. In many cases pneumonia patients whose symptoms are not life-threatening would be candidates to receive oxygen via an oxygen concentrator which is less expensive.
Oxygen supplementation is one way to help patients who cannot breathe adequately on their own. Purpose of review. Oxygen saturation 90 arterial oxygen partial pressure 60 mm Hg on room air or with low-flow supplemental oxygen via nasal cannula or return to baseline oxgen level for patients.
We review the evidence on the use of noninvasive respiratory supports noninvasive ventilation and high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy in patients with. High-flow nasal oxygen versus conventional oxygen therapy in patients with COVID-19. It is not mentioned whether there was a subgroup of COVID-19 pneumonia patients treated with FiO2.
It eliminates wastage and maximizes oxygen for pneumonia. The normal flow rate of oxygen is usually six to 10 litres per minute and provides a concentration of oxygen between. The reason they did not receive tocilizumab and why.
This type of oxygen therapy is.

Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy And Noninvasive

Administration Of Supplemental Oxygen Nejm

High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy In Adults Physiological Benefits Indication Clinical Benefits And Adverse Effects Respiratory Care
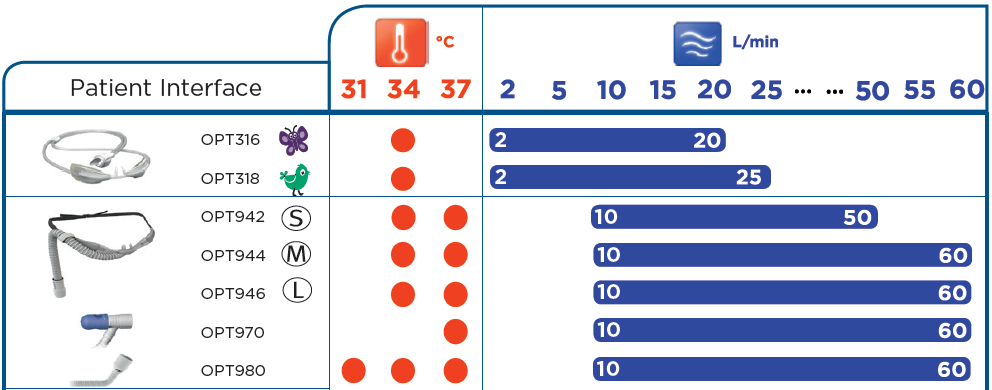
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

Oxygen Therapy For Children A Key Tool In Reducing Deaths From Pneumonia Graham 2020 Pediatric Pulmonology Wiley Online Library

Environmental Contamination In The Isolation Rooms Of Covid 19 Patients With Severe Pneumonia Requiring Mechanical Ventilation Or High Flow Oxygen Therapy Journal Of Hospital Infection

Cureus High Flow Nasal Cannula Mechanisms Of Action And Adult And Pediatric Indications

Covid 19 Pneumonia Guiding The Decision To Intubate Based On Work Of Breathing Assessment Independent Of Oxygenation
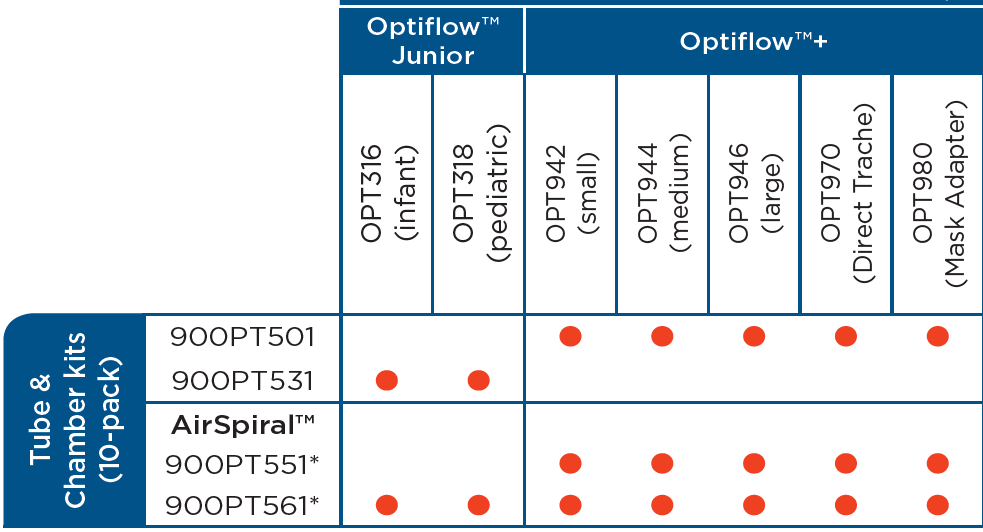
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

High Flow Therapy When And How Don T Forget The Bubbles
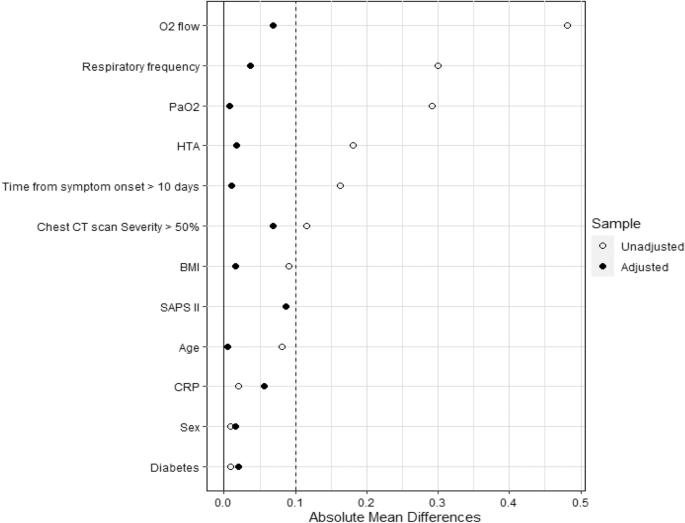
High Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy To Avoid Invasive Mechanical Ventilation In Sars Cov 2 Pneumonia A Retrospective Study Annals Of Intensive Care Full Text

Covid 19 Respiratory Care Of The Nonintubated Hypoxemic Adult Supplemental Oxygen Noninvasive Ventilation And Intubation Uptodate

Reservoir Cannulas For Pediatric Oxygen Therapy A Proof Of Concept Study

Comparison Of High Flow Nasal Cannula Versus Oxygen Face Mask For Environmental Bacterial Contamination In Critically Ill Pneumonia Patients A Randomized Controlled Crossover Trial Journal Of Hospital Infection

Six Month Follow Up Chest Ct Findings After Severe Covid 19 Pneumonia Radiology

Heated Humidified High Flow Oxygen For Respiratory Support A Review Of Clinical Effectiveness Cost Effectiveness And Guidelines Ncbi Bookshelf

Nasal High Flow Oxygen In Acute Respiratory Failure Sciencedirect
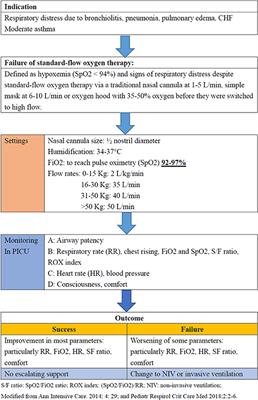
Frontiers High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy In Children With Acute Respiratory Distress With Hypoxia In A Pediatric Intensive Care Unit A Single Center Experience
